The Intricacies of Cycling and Float in Lithium Batteries
Introduction
Lithium batteries, with their high energy density and versatility, have gained paramount importance in various applications such as portable electronics and electric vehicles. This blog delves into the concepts of cycling and float charging, key to optimizing their performance and longevity.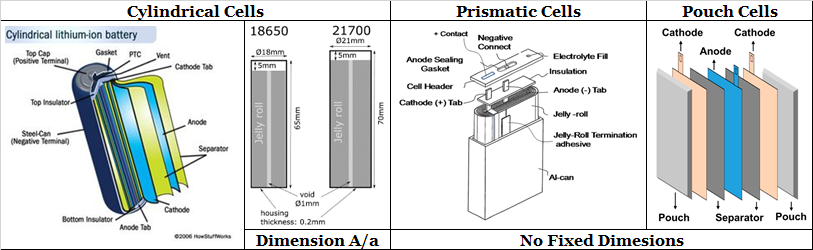
Cycling Lithium Batteries
When a lithium battery is on cycling, it is engaged in repetitive charge and discharge cycles. This activity is typical in applications where the lithium battery is used regularly, such as in electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems.
Float Life of Lithium Batteries
On float refers to maintaining a lithium battery at a relatively constant voltage, typically slightly below its maximum, to keep it fully charged and ready for use. However, floating is not recommended for lithium-ion batteries as it may lead to safety hazards and a reduced lifespan.
Comparative Study of Float Vs. Cycling
Battery charging strategies differ according to application needs. Float charging is suitable for batteries in standby systems, while cycling is essential for applications requiring regular energy use.
Pointers for Battery Life
To prolong the life of a lithium battery, it is crucial to follow the manufacturer's guidelines and optimize charging strategies, balancing factors such as charging speed, energy efficiency, and longevity.